The global games market (all platforms: mobile, PC, console, cloud, etc.) is projected to grow steadily through 2030. One report estimates the market could hit ≈ USD 505 billion by 2030 (from ~USD 298 billion in 2024), implying a CAGR of ~ 8.7%.
The gaming business has transformed itself to become one of the most dynamic, innovative, and lucrative industries worldwide. Behind all the successful mobile games, console games, VR, or indie games is an organized and well-thought-out workflow. It is important to understand the processes of developing a video game even when one is a beginner, an indie developer, or a large studio. These phases determine how an idea is turned into an interactive one and enjoyed by millions.
This guide will cover all the stages of video game development, starting with the concept and going all the way to the post-launch maintenance. Knowing these steps, you will have an idea of what the planning, production, testing, launch, and maintenance of the game will be in the long run. Efficiency, cost savings, and a smooth final product can be achieved by having proper knowledge of these stages.
6 Main Stages of Video Game Development
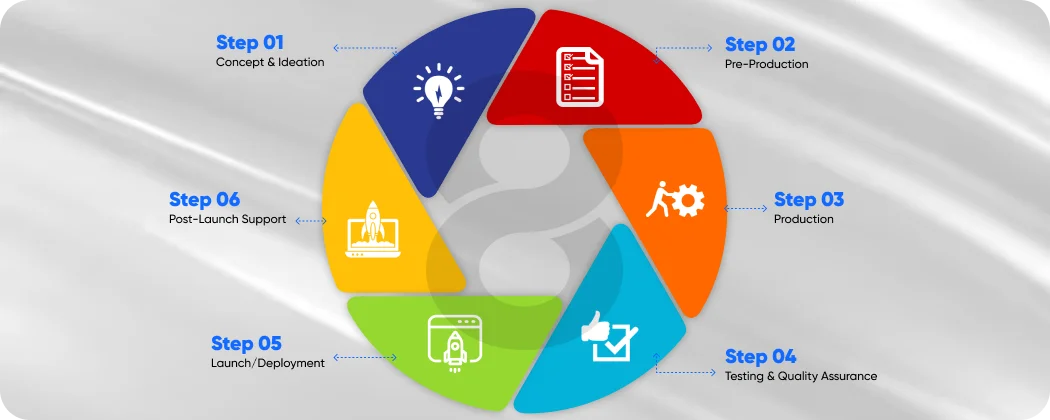
The video game development cycle resembles movie-making or software development, with some complexity added because of gameplay and graphics and interactive narration. Although projects are all different, there are usual steps in video game development, and these are:
- Concept & Ideation
- Pre-Production
- Production
- Testing & Quality Assurance
- Launch/Deployment
- Post-Launch Support
Each phase has its own duties, achievements, and challenges. The knowledge of such stages helps in avoiding time wastage, minimizing expenses, and maintaining innovative ideas during the process.
Stage 1: Concept & Ideation
All the games start with an idea. Such a spark may be a character, a gameplay element, a plot, or even a visual style. At the concept stage, the aim is to establish the nature and the direction of the game.
These are the key questions that developers are interested in: What is the gameplay loop? Who is the target audience? What platforms will the game be released on? Definite answers mean that there will be no confusion in the future, and the project will have a clear scope.
The common activities in this stage are:
- Brainstorming gameplay and features
- Drawing crude people, settings, and ideas
- Determining target platforms and audience
- Taking into account such monetization as free-to-play or premium
The key deliverable would be the game concept document, which would be a brief reference document about the vision of the game, the core gameplay, the target audience, and the market potential. Though short, it is the basis of all future stages of the development of video games.
Stage 2: Pre-Production
After the idea is sound, pre-production comes in. This phase authenticates the concepts and makes sure that the project is technically and creatively viable. Pre-production is a method that decreases the risk since potential problems can be identified at an early stage, and the teams can make accurate plans.
At this stage, groups come up with prototypes in order to test fundamental mechanics, experiment with plots, and generate concept art. The game engine selected by the developers, such as Unity Game Development, Unreal, and Godot, also depends on the requirements of the project. This is where the game design document (GDD) comes in, which describes:
- Mechanics and controls of the game
- Level and world design
- Plots, dialogue, and narration
- UI/UX and visual style
- Environmental designs and characters
Prototyping enables the teams to find fun, scalability, and technical problems. Pre-production discourages waste of time in production and ensures that the game is done according to the original vision.
Stage 3: Production – Making the Game a Reality
The stages of video game development are production, the most resource-consuming and the longest one. This is where concepts get implemented into content. The game is developed by a number of teams, including programmers, artists, animators, sound designers, and narrative experts.
Programming forms the technical base, such as:
- Game logic and controls: Controls of players
- Artificial intelligence behavior and mechanics of enemies
- Collision systems and physics
- Multi-user networking and server integration
- UI and interaction systems
Artists and animators create characters, settings, props, visual effects, surfaces, and animation. In the meantime, sound designers compose music, produce sounds, record voices of characters, and design ambient sounds. Sound enhances the immersion and the general experience of the game.
Level designers make sure that gameplay movement is logical, both in terms of difficulty and interaction with players. Narrative designers ensure gameplay and storytelling remain seamless, making the two indistinguishable. Developers repeat the production process continuously, maintaining constant communication and problem-solving to guarantee quality at every stage of video game development.
Stage 4: Testing and Quality Assurance
In any game development work, testing plays an imperative role. QA is used in the development phases of the video game to make sure that the players have a game that is flawless and without bugs.
Significant testing activities are:
- Functional Testing: The mechanics are correct and without errors.
- Interoperability Testing: Verifies compatibility on devices, operating systems and hardware.
- Performance Testing: Tests how FPS remains stable, load times, memory usage, and energy usage.
- Playtesting: It involves the utilization of actual players to test enjoyment, difficulty, controls, clarity of the story, and the game flow.
Feedback cycles are crucial. This is because developers have found that playtesting uncovers more than months of in-house testing. The individual iteration of these results does enhance gameplay, balance, and engagement, which are essential objectives in the development stages of the video game.
Stage 5: Launch and Deployment
To successfully launch a game, one has to prepare other than to write a program. The stage of launching the game makes sure that the game becomes available to the players, with a minimum of problems.
Preparation tasks include:
- Last-minute bug fixes and optimization
- Platform-specific adjustments
- Submission to PCs, consoles or app stores
- Advertising, trailers, and advertisements on social media
Stage 6: Post-Launch Support
The development of the game does not stop at the launch stage. The services provided after the release are necessary to keep the players interested, solve problems, and prolong the gaming experience. It is a critical phase in the contemporary markets where LiveOps, seasonal events, and downloadable content (DLC) make money and retain the players.
Tasks in Post-Launch Support
- Bug Fixes and Updates: fixing bugs and performance optimization on different devices.
- Content Expansion: Introducing new levels, characters, storylines, or cosmetic effects to make the experience new.
- LiveOps & Events: Organize player games, challenges, or competitions with a time limit to keep players interested.
- Community Management: Engaging the players via social media, forums, in-game messaging to develop loyalty.
- Monetization Management: To optimize the revenue without damaging the experience of the players, balancing between in-game purchases, subscriptions, and ads is needed.
This is a critical stage in both the 2D and 3D games but the size varies. Small 2D games can have their updates published frequently, whereas AAA 3D games can have a major expansion or a season.
The global video games market size was estimated at USD 274.63 billion in 2024 and it is projected to hit around USD 721.77 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 10.15% during the forecast period 2025 to 2034.
Tools and Technologies

The appropriate choice of tools simplifies the production process at all stages of the creation of video games.
- Game Engines: Unreal Engine, CryEngine, Unity, Godot.
- Art/Animation Software: Blender, Maya, Photoshop, Substance Painter.
- Project Management Software: Jira, Trello, Asana.
These tools enable teamwork, an element of providing version control, asset management, and action-packed workflow.
Read More: How to Make a Video Game
Roles in Game Development
The efficient work of the game development demands collaboration with the specialists:
- Game Designers
- Programmers
- Artists and Animators
- Sound Designers, Composers
- Narrative Designers
- QA Testers
- Community Managers
- Marketing and Producers
Every role has its own role during the stages of development of the video game, which brings continuity between the conception and the post-start phases.
Timeline of Game Development
The time of development is dependent on the complexity of the project:
- Hyper-casual mobile games: 2-4 months
- Indie games: 1-3 years
- AAA titles: 3-6+ years
Knowing timelines gives a chance to plan realistically every stage, allocation of resources, and setting of milestones.
Common Challenges in Video Game Development

The development of games has its own problematic issues:
- Scope Creep: Growing concepts lead to the derailment of schedules.
- Budget Overruns: It can be paralyzed by miscalculations.
- Technical Limitations: Hardware or engine restrictions necessitate a change.
- Balancing Fun and Function: Game tuning is not always as quick as it can be.
- LiveOps Complexity: It takes continuous effort to maintain long-term engagement.
It is important to be aware of these barriers to ensure the video game development stages are achieved successfully.
Tips for Beginners
Amateurs can enhance their probability of success by:
- Against small and manageable projects
- Comprehensive knowledge of one engine
- Early prototyping and iterating
- Doing small games first and then starting to do big projects
- Creating a work portfolio to present the work done
The earlier one masters the stages of video game development, the more efficient, confident, and skilled one becomes.
“Video game development is where imagination meets engineering; each stage transforms an idea into an interactive experience that captivates, challenges, and connects players across the world.”
– Roshaan Faisal, Business Development Head at 8ration
Build Your Next Video Game with 8ration

Video game production cycles transform imaginative ideas into interactive and real-life experiences. A well-structured workflow ensures efficiency, clarity, and quality, following the stages of pre-production, production, testing, launch, and post-launch. At 8ration, we have extensive experience in the phases of video game development, and this understanding allows us to help developers manage resources efficiently, maintain a clear creative vision, and create games that captivate players across the globe.
Through such measures and a continuous learning process in each project, the developers will be able to design an engaging, winning, and highly lucrative game in both the 3D and 2D gaming mediums.